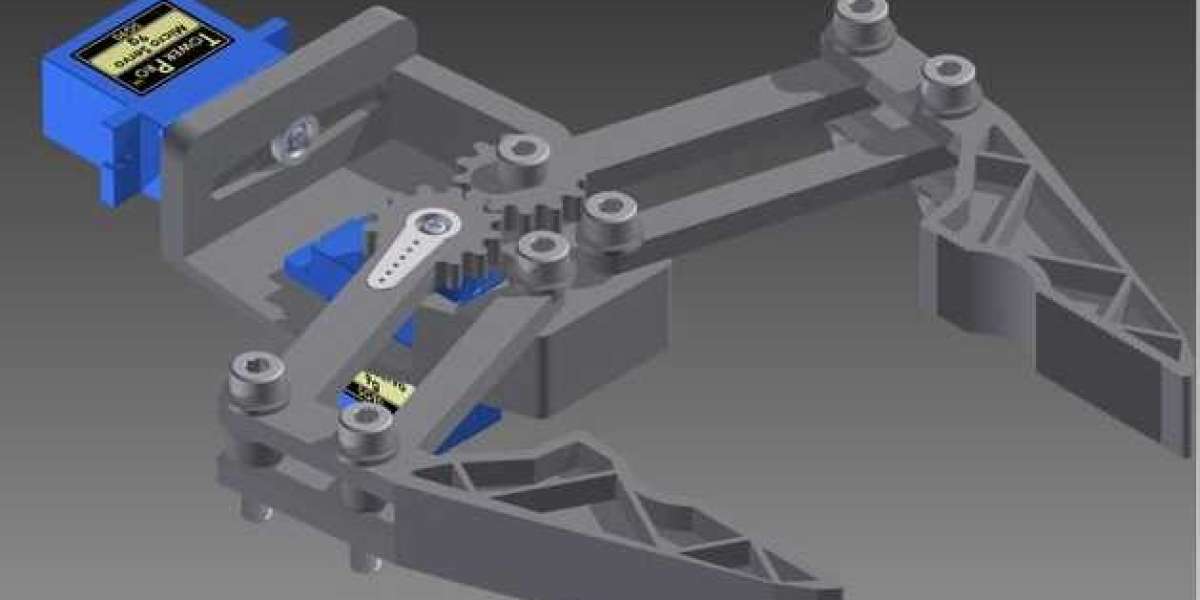
The Power of Precision: Exploring the World of Mechanical Grippers
In the world of robotics and automation, the humble mechanical gripper plays a pivotal role in transforming complex tasks into efficient, repeatable actions. These versatile devices have become indispensable in a wide range of industries, from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and beyond. In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating world of mechanical grippers, exploring their design, functionality, and the myriad applications that make them an integral part of the modern industrial landscape.
Understanding Mechanical Grippers
A mechanical gripper is a robotic end-effector designed to grasp, manipulate, and handle objects of various shapes, sizes, and materials. Unlike their pneumatic or hydraulic counterparts, mechanical grippers rely on mechanical components such as gears, cams, and linkages to perform their gripping tasks. This mechanical simplicity offers several advantages, including precision, durability, and ease of control.
Design and Components
Mechanical grippers come in a variety of designs, each tailored to specific applications. However, they generally consist of several key components:
- Jaws or Fingers: The most visible part of a mechanical gripper, the jaws or fingers, come in different shapes and materials depending on the intended use. Some grippers have two opposing fingers, while others use three or more fingers to achieve a secure grip. Soft, compliant materials like rubber or foam may be used to grip delicate objects, while rigid materials are ideal for heavier items.
- Actuators: Actuators are responsible for the opening and closing of the gripper's jaws. Common types include electric motors, servos, or pneumatic cylinders, depending on the gripper's design and requirements.
- Linkages and Mechanisms: These components translate the motion generated by the actuators into the precise movement needed to open and close the gripper. Mechanical linkages, cam systems, or gears can be used to achieve this.
- Sensors: Grippers often incorporate sensors to provide feedback on the gripping force, object position, and overall status. This information allows for fine-tuning of the gripping process and ensures safe and efficient operation.
Functionality
The primary function of a mechanical gripper is to securely grasp and manipulate objects. Their capabilities vary widely, from delicate, high-precision operations in industries like electronics manufacturing to heavy-duty tasks in construction or automotive assembly. Mechanical grippers offer benefits such as:
- Precision: Mechanical grippers are renowned for their accuracy, making them ideal for applications where objects must be handled with extreme care and precision.
- Versatility: These grippers can be adapted for various tasks by changing the shape, size, or material of the fingers. They can handle a wide range of objects, from small and fragile components to large, bulky items.
- Reliability: Mechanical grippers are known for their robustness and durability, making them a dependable choice for industrial applications that require continuous operation.
Applications
The applications of mechanical grippers are vast and continue to expand as technology evolves. Some key industries and use cases include:
- Manufacturing: Mechanical grippers are essential in assembly lines for picking, placing, and manipulating parts and products.
- Material Handling: They are used in warehouses and distribution centers to load and unload items, sort packages, and stack goods.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: Grippers are employed in surgical robots and pharmaceutical production for precise handling of delicate instruments and components.
- Electronics: In the electronics industry, they assist in circuit board assembly, semiconductor handling, and precision testing.
- Aerospace: Mechanical grippers play a crucial role in aircraft assembly, handling delicate and heavy components alike.
- Agriculture: In automated agriculture, grippers help with tasks such as fruit picking and crop handling.
Conclusion
Mechanical grippers are the unsung heroes of automation, quietly but efficiently performing tasks that would be laborious or impossible for humans alone. Their precision, versatility, and reliability make them indispensable in numerous industries. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications for these mechanical marvels, further revolutionizing the world of automation and robotics.